American Black Bear
Scientific Name: Ursus americanus
Type: Mammal
Family: Ursidae (Bear)
Size: 5 to 6 foot long
Weight: 200 to 600 pounds
Life Span: 20 years
Physical Description
Black bears are most often black in color with a pale muzzle and sometimes a white chest spot. Bears in the eastern portion of North America usually black. However, in the western portion of the country, they tend to be lighter in color — brown, cinnamon, or blonde.
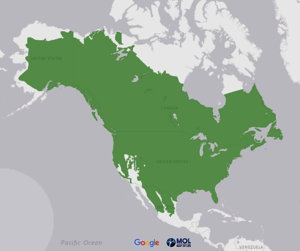
Range and Habitat
American Black Bears are found in the forested areas of the United States, Canada, and Mexico. They prefer areas with lots of ground cover and abundant food. In addition, they need a place with a cave or large overhanging rocks that can be used as a den for winter.
Diet
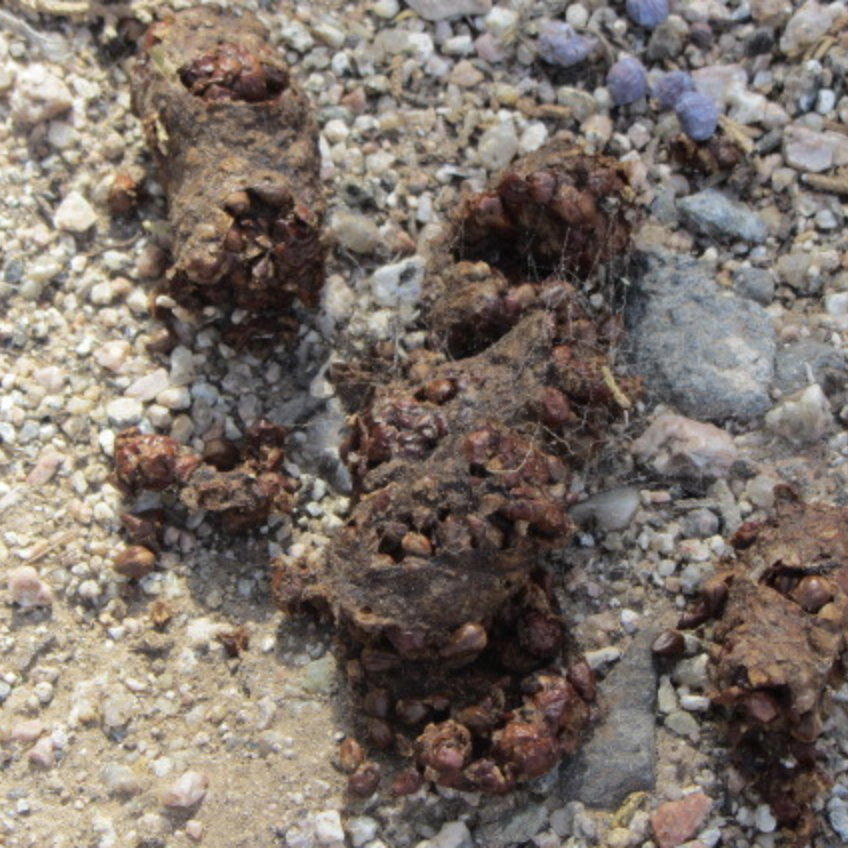
Black bears will eat almost anything. They eat whatever is plentiful including insects, eggs, fish, and occasionally small mammals. They will also eat dead animals and garbage. However, 95% of their diet is plant-based such as roots, buds, nuts, berries, and fruits.
Black Bears love honey and will rip open a tree to reach the nest inside. They will also break apart wooden beehives to get to the honey.
Behavior and Social Life
Bears are generally active in the early morning and evening but may be active during the day in areas where human food sources are available.
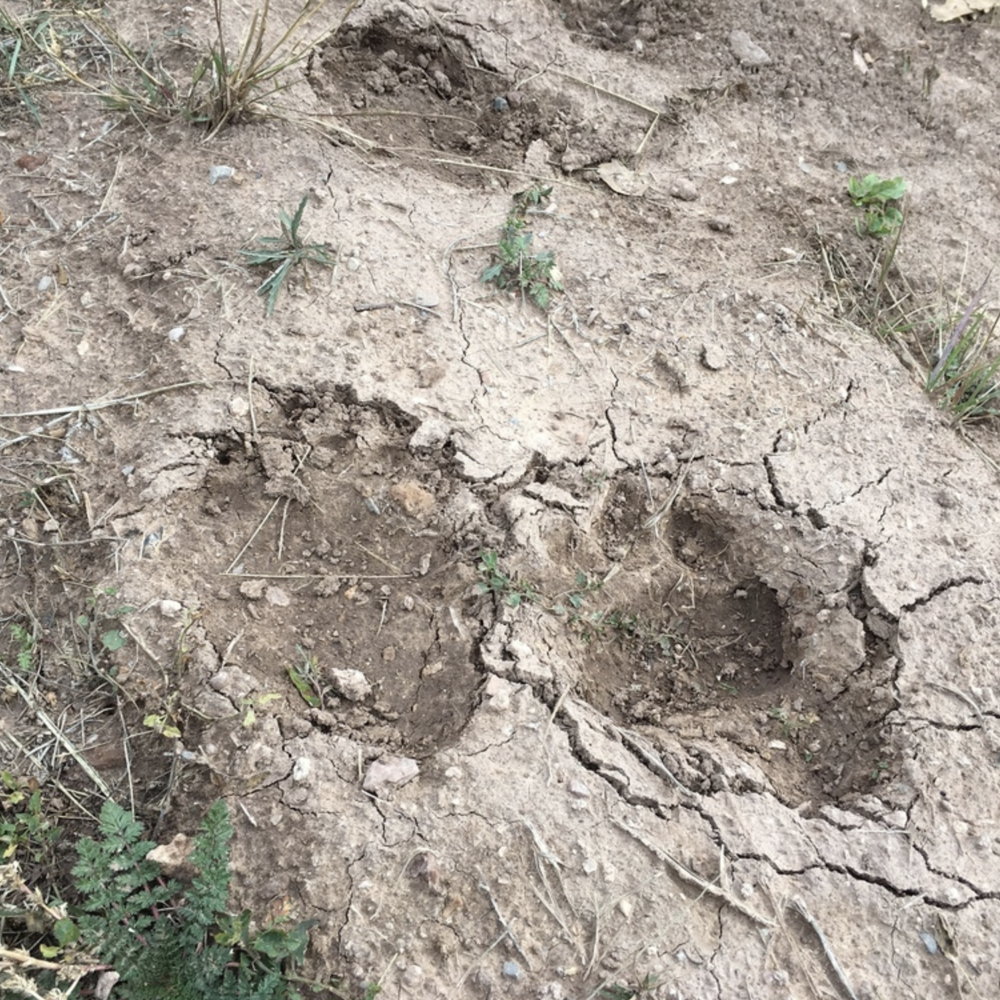
American black bears, particularly cubs, are good at climbing trees very quickly. Their claws are hooked helping them to grip the bark. To get down to the ground, a bear will back down the tree.
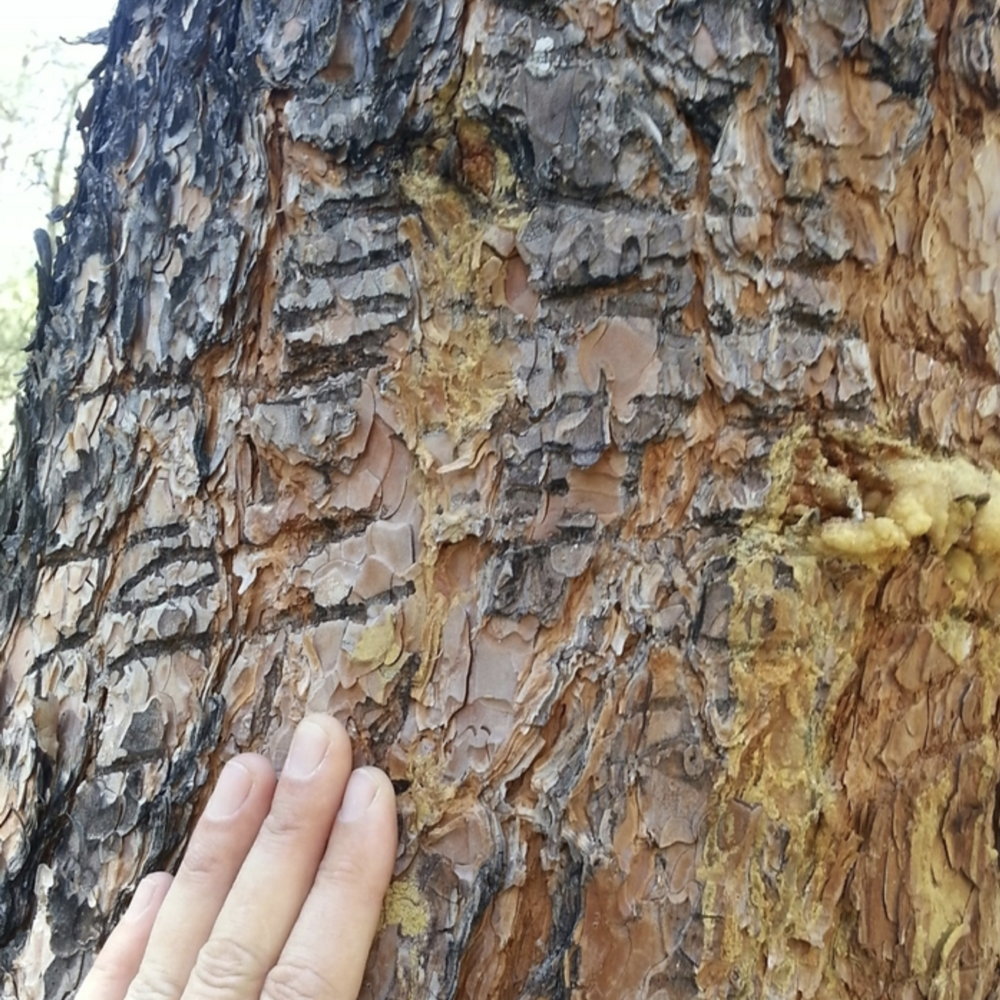
Bears communicate in a variety of ways using body and facial expressions, sounds, touch, and scent marking. In addition, they will make claw marks on tree trunk to advertise their presence.
During most of the year, black bears rest in bed sites that are shallow depressions in the forest leaf litter. In the fall, they seek out a sheltered place or den to spend the winter such as a cave, rock overhang, or an area dug out under the roots of a large tree.
During winter, black bears enter a state of dormancy called torpor. This, unlike true hibernation, means that bears may be active at times even in the middle of winter.
Looking for Food
Grunting
Title
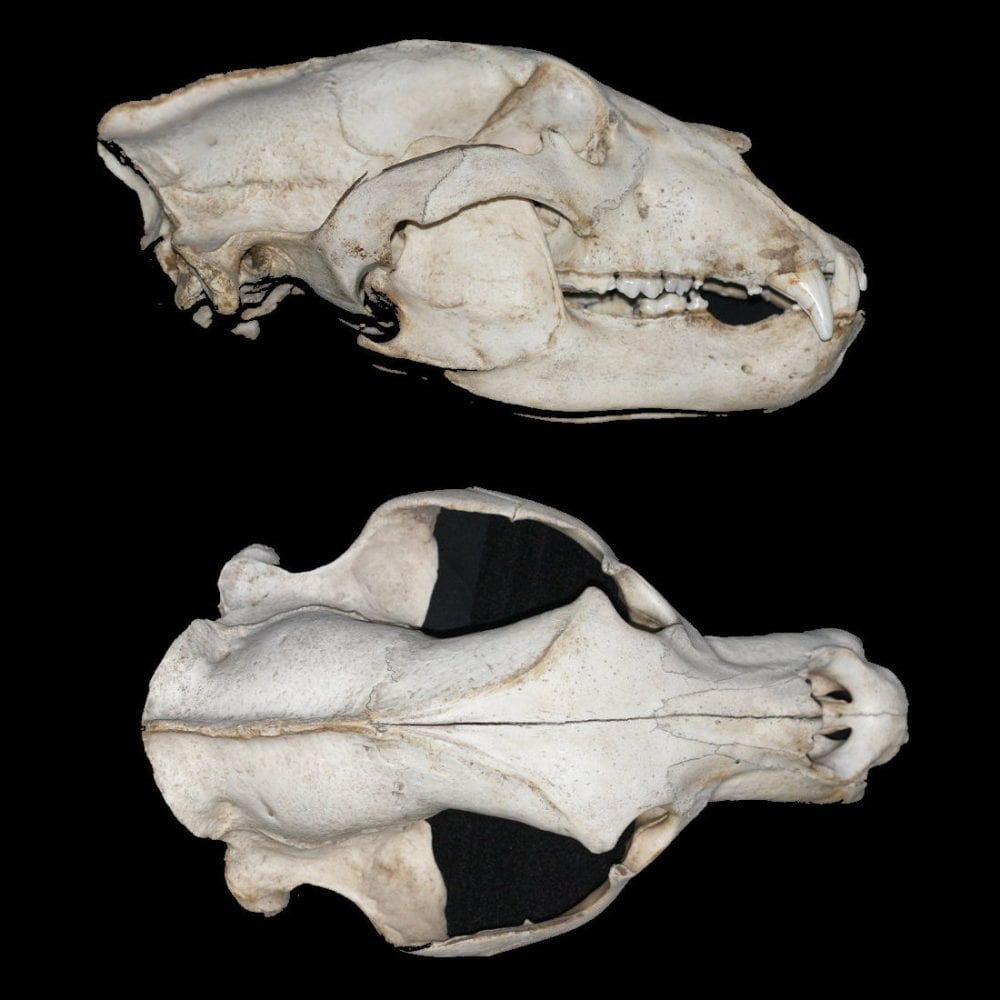
Skull
Claw Marks

Life Cycle
Black bears are usually solitary, with males and females only briefly coming together to mate in the early summer. Females usually give birth to two or three cubs every other year. The cubs are typically born in January and live with their mothers for up to two years. The cubs are born in the den and only emerge in the spring with their mother.
Ecological Role
Black bears play an important role in the environment. They help to disperse the seeds of the plants they eat and control insect populations by consuming large numbers of larvae and adults.
Interactions With Humans
Black bears are considered game animals in many areas and are hunted for their meat and fur as well as for the sport.
They are usually shy and rarely attack humans unless threatened. However, they can become a nuisance by knocking over garbage cans and breaking into cars and houses to get to food.
Interesting Facts
- Bears can walk short distances on their hind legs
- They are one of the most intelligent animals in North America
- Bears can run up to 25 miles per hour
- In freshwater, black bears are able to paddle for over a mile
- Black bears may forage up to 20 hours a day when preparing for winter
- A black bear may lose up to 30 percent of its weight during winter
- Black bears have a keen sense of smell
More Information
Mammal Guide
Track Guide
PEEC News – Getting to Hibernation
PEEC News – What Can We Learn From a Black Bear’s Skull?
PEEC News – What to Do if You See a Black Bear
Nature News – Be Bear Away: Keeping Our Black Bears Safe
Nature News – Super Sleepers
Nature Notes – Bears — An Inside Story
PEEC Live-streamed Talks – Backyard Bears
PEEC Live-streamed Talks – Bears in New Mexico