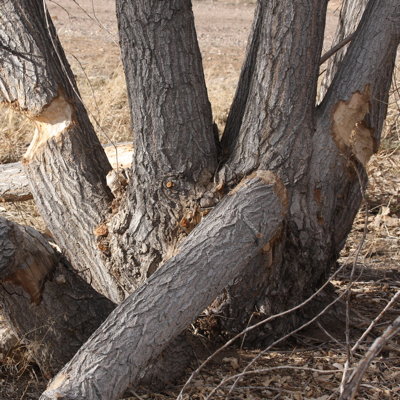
North American Beaver
Scientific Name: Castor canadensis
Type: Mammal
Family: Castoridae (Bear)
Size: 29 – 35 inches long plus 8 – 13 in tail
Weight: 90 to 110 pounds
Life Span: about 16 years
Physical Description
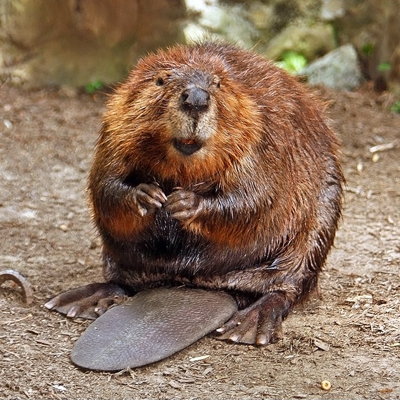
North American beavers are adapted for survival in water. They have a glossy, reddish brown or blackish brown coat which is waterproof; there is an undercoat with fine hairs which increases the warm of the coat. They have short, round ears and nostrils that can close to keep the water out. Their large, flat, paddle-shaped tail and webbed hind feet aid in swimming.
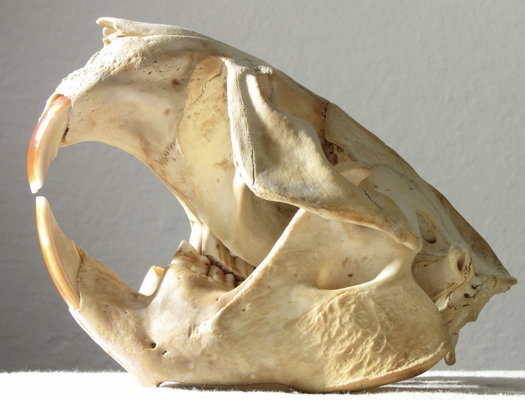
North American beavers have short front legs and longer back legs causing them to have a rear end that is higher than the front while walking. In addition, they have skulls and teeth that are very large. Their incisors are crucial for cutting through hard woods and grow throughout the beaver’s lifetime.
Tail and Webbed Feet

Skull and Teeth
Range and Habitat
North American beavers have a range that covers almost all of the continent with exception for the northern reaches of Canada and the desert areas of the southern US and Mexico.
Beavers are semi-aquatic and live near ponds, lakes, rivers, and streams. They build homes out of branches and mud called lodges. Lodges are built either on an island or on the bank/shore of a body of water. Often a lodge can only be accessed from underwater.
Lodge
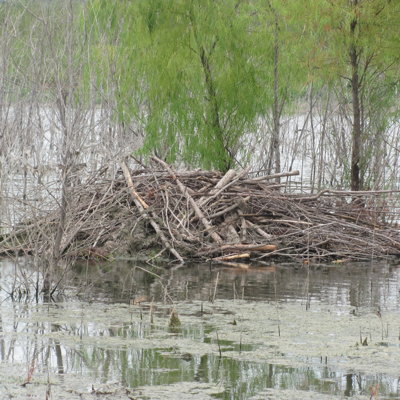

Diagram of Lodge

Diet
North American beavers are herbivores, eating leaves, woody stems and aquatic plants. They eat the bark and soft wood underneath the bark of the materials they use for building: maple, willow, beech, birch, alder, and aspen trees.
They store branches at the bottom of their chosen body of water for use throughout the winter. The cold water preserves the nutritional value of the food. Beavers hold their food in their front paws and eat it like a corn-on-the cob.
Behavior and Social Life
Beavers tend to live in groups called colonies with their relatives. The yearlings stay with their parents for up to two years while helping to take care of various chores like food collection, dam building, and rearing new kits. Different families do not interact with each other.
Beavers are primarily nocturnal and semi-aquatic. If seen during the day, it is mostly around dusk. They will travel a good distance from their lodge to find food and will build a canal as a way to float food back to home if a good source is found.
These animals primarily build dams to slow down the water flow and provide stability for their lodges. The dams are engineered to match the speed of the water — straight for slow water and curved for faster.
Beavers communicate in a variety of ways. They will mark their territory using a musk-like substance called castoreum. They call out to others with a low, groaning sound. They also use particular postures to communicate to family members. Their tail is used as a warning signal when slapped against the water.
Title
Life Cycle
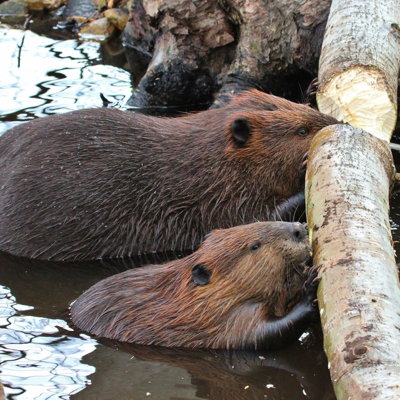
Beavers are monogamous, staying together with one mate as long as it lives. The females give birth to one litter each year, usually between April and July. When born, baby beavers or kits have all of their fur and open eyes. The kits will usually be weaned at about two weeks of age but remain in the lodge for a few weeks more.
Older young known as yearlings remain as part of the family until driven off at around two years of age, just before a new litter is born. They will start their own colony, starting to breed at about three years old.
Adult and Child

Ecological Role
Beavers play an important role in the environment by building dams. These dams help create habitats for many aquatic organisms, maintain the water table at an appropriate level, and prevent flooding and erosion.
However, beaver dams can slow the flow of water in fast streams enough to result in the deposit of silt. In addition, a dam can adversely effect the some of the other wildlife in the area.
Interactions With Humans
On the positive side, trading in beaver fur has been a lucrative business in the last century. On the negative side, beaver dams may cause flooding in low-lying areas and loss of valuable timber.
Interesting Facts
- There are two species of beaver (North American and European) which are similar but not genetically compatible.
- North American beavers are one of the largest rodent in the world.
- The Nez Perce tribe used to make beaver teeth necklaces.
- There were giant beavers during the Ice Age that were up to 8 feet long.
- The beaver secretes a chemical compound from a sac under its tail that smells like vanilla and is approved as a natural flavoring by the FDA.
- New dams are usually started by a young male beaver looking for a mate or a newly mated couple.
- A beaver’s front teeth are orange due to the iron they contain.
- A beaver’s tail is used as a rudder while swimming, a signal when slapped on the water to warm others of danger, and a prop on land to let the beaver sit upright.
- Beavers have a set of transparent eyelids that help them see underwater.



















